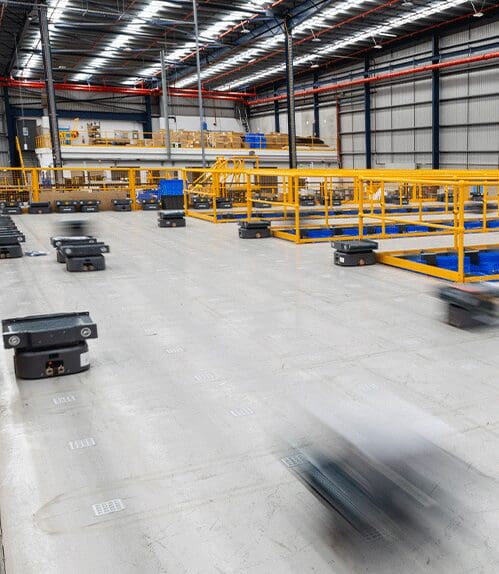
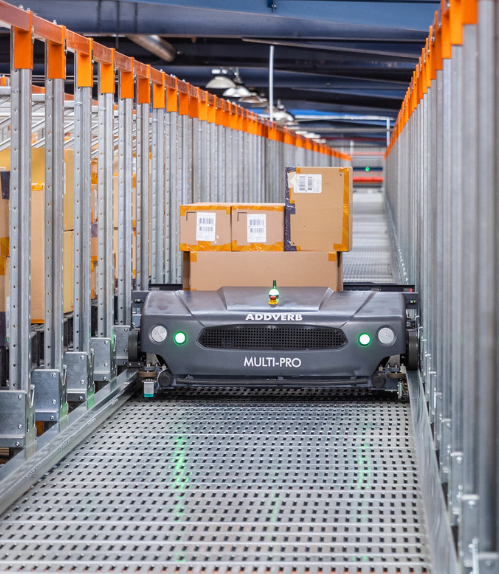
Table of Contents
What is Warehouse Automation?
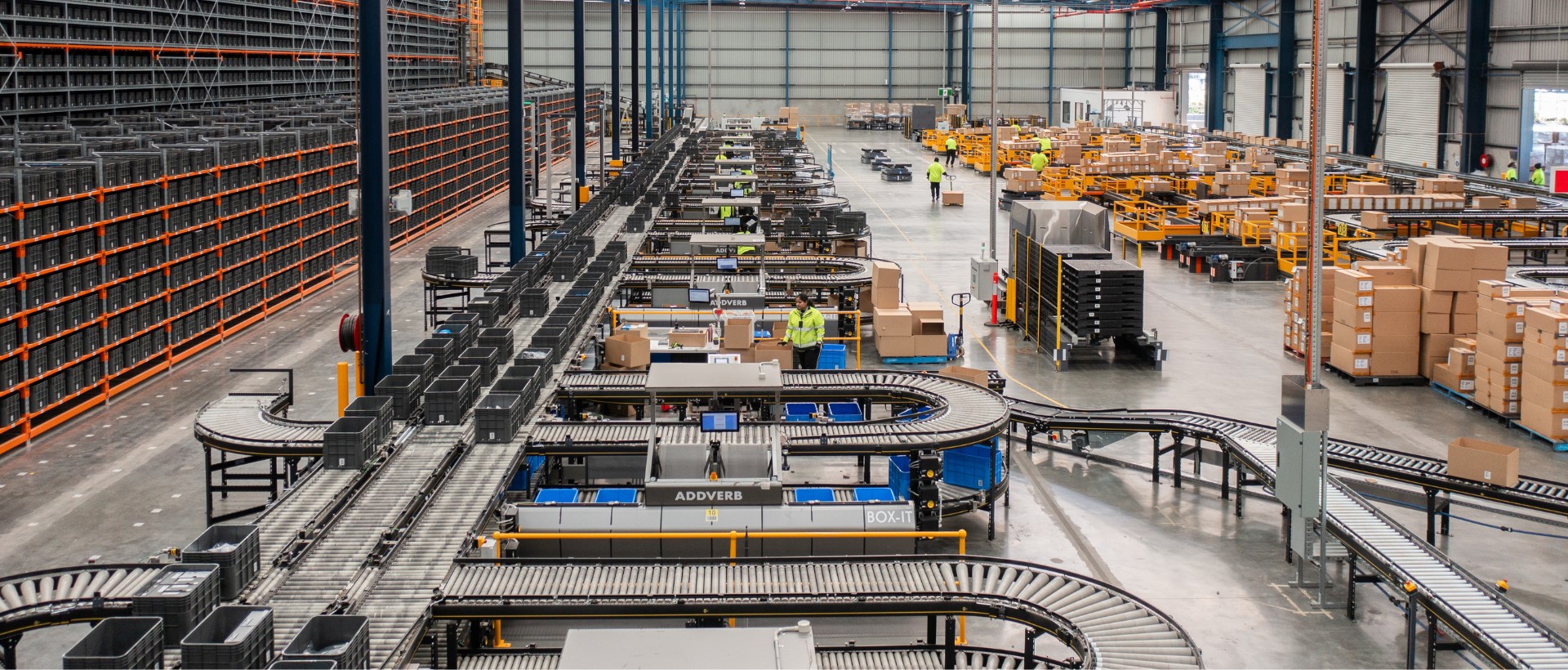
Warehouse automation involves using technology to streamline operations and increase efficiency. It includes robotics, AI, and IoT devices to perform tasks previously done manually.
The goal is to improve productivity, accuracy, and overall effectiveness. Automation allows warehouses to operate 24/7, reducing processing time and costs, and handling increasing inventory from e-commerce and global trade.
Let us see the importance, why, and how warehouse automation can help your business grow.
Importance of Warehouse Automation
Enhanced Productivity
Automated systems function at a consistent pace, resulting in enhanced productivity. Automating warehouses allows human workers to devote their attention to more complicated duties, thus increasing warehouse efficiency.
Improved Accuracy
Automation methods reduce the occurrence of human errors dramatically. This is especially important in operations like order picking, when even minor errors can result in costly consequences, such as delivering the wrong product to a customer.
Space Optimisation
Smart warehousing enables more efficient use of available space. Compact automated technologies, such as vertical storage solutions and robotic palletisers, aid in increasing storage capacity while reducing waste.
Cost Reduction
While the initial investment in warehouse automation solutions may be significant, the long-term cost reductions are enormous. Labour costs are reduced, error rates are reduced, and inventory management is enhanced, resulting in total cost-efficiency in warehouse operations.
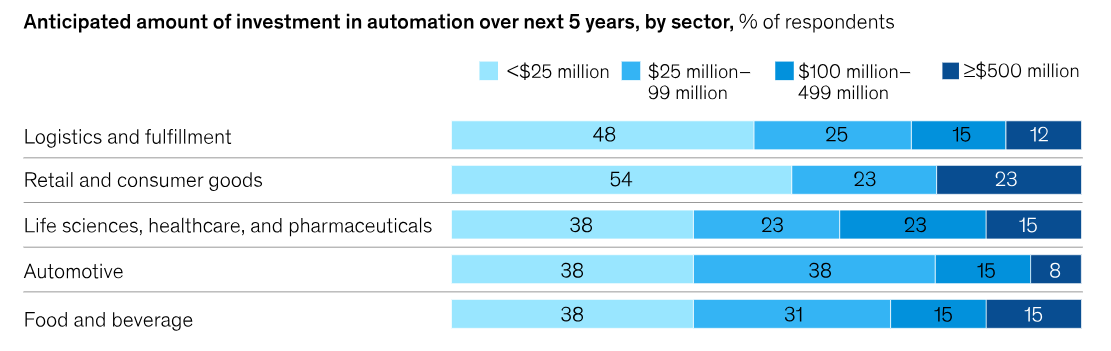
Companies plan to increase their investment in automation significantly over the next five years, reaching 25 percent of capital spending on average. In logistics and fulfillment, automation is expected to account for more than a third of capital spending, the largest fraction of any sector.
Source: McKinsey & Company
Explore tailored automation solutions, connect with our experts today!
Benefits of Warehouse Automation
- Faster Order Fulfilment: Automated picking and packaging processes speed up order fulfilment, allowing warehouses to meet tight delivery schedules and match customer expectations for on-time delivery.
- Track of Inventory Levels: Inventory levels are visible in real-time due to automation systems outfitted with sensors and IoT devices. This enables precise inventory tracking, reducing stockouts, and overstock situations.
- Error Reduction: Human errors, such as mispicking or misplacing items, can be costly and detrimental to consumer happiness. Automation in the warehouse decreases these errors dramatically, resulting in higher order accuracy.
- Increased Safety: Automation systems can undertake heavy lifting, lowering the danger of injury to human workers. Furthermore, they can be programmed to collaborate with humans.
- Scalable: Many warehouse automation solutions are modular and scalable, allowing firms to adjust and extend their operations in response to changing demands and requirements.
- Data-Driven Strategy: Automation systems create massive volumes of data, which may be analysed to get useful insights into warehouse operations.
Ready to transform your operations with advanced automation solutions, enhancing accuracy and safety while enabling data-driven decision-making? Contact Addverb today!
Key Components of Warehouse Automation
A robust warehouse automation system is made up of several critical components. Each component is essential in converting old warehouses into high-tech, efficient operations. The following are the essential components:
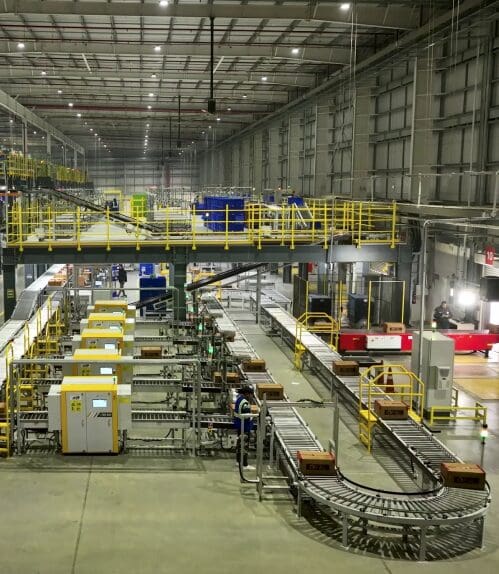
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
ASRS automation systems are made up of racks, shelves, and cranes or robotic shuttles that automatically store and retrieve objects from preset storage places. These systems handle inventory management and order picking with ease.
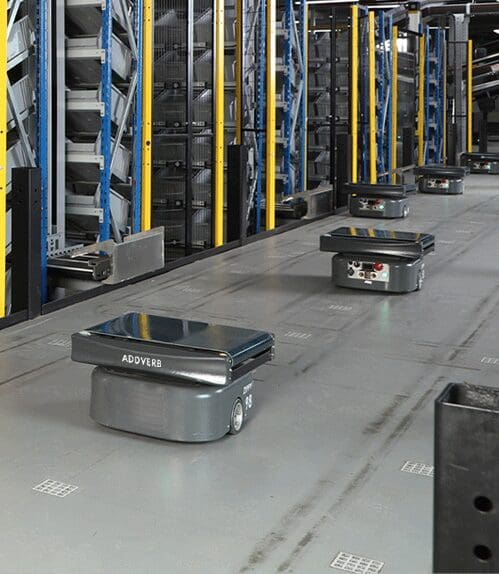
Mobile Robot
Mobile Robots are important for automating the warehouse. These intelligent devices can conduct a variety of operations autonomously, including picking, sorting, and delivering goods.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs are sorting robots that deliver goods along specified tracks within a warehouse. They have sensors for obstacle avoidance and can transport large or heavy goods efficiently.
Conveyor Systems
Conveyor systems make moving items across the warehouse easier, minimising the need for physical handling. They link processing areas like receiving, picking, packaging, and shipping.
Software
Softwares serves as the central processing unit, coordinating and managing the flow of items and information in the warehouse. It allows smooth communication between various automated systems, improving overall performance.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) Technology and Barcode Scanning
Barcode scanners and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology are used to properly track and identify inventory goods. These technologies deliver real-time data to improve inventory management.
How Warehouse Automation Works
Warehouse automation utilizes technology to improve warehouse efficiency and improve operations. It involves integrating advanced technologies such as robotics, AI (artificial intelligence), IoT (Internet of Things), software solutions, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to undertake activities that have been done by people. Automation is an effective method for improving efficiency by reducing human error, improving inventory management, speeding up order fulfilment, and improving productivity. To automate a warehouse, businesses start with an analysis of their operation, selecting the correct technology, visualising the system, and implementing a solution, step by step. The right automation strategy provides for seamless integration, significant efficiencies, and longevity in operational cost reductions.
- Receiving: When items arrive at the warehouse, barcode or RFID technology is used to scan and log them into the inventory management system. The items are subsequently stored in designated areas of the warehouse.
- Selecting: When a customer puts an order, the warehouse management system (WMS) gets the information and sends it to the automation system. The WMS then finds the most effective methods of selecting and packing.
- Picking: Automated systems, such as AS/RS or robotic pickers, extract things from storage. AMRs or AGVs are sometimes used to move things to a specific packing area.
- Packing: Sort and pack things according to order specifications using automated packing machines. Advanced systems can handle various packaging materials and adjust to diverse product sizes.
- Quality Control: Before items are dispatched, automated quality control systems guarantee that they are accurate and free of flaws. This process reduces the possibility of returns and client complaints.
- Shipping: After the order has been completed and quality-checked, the automated system arranges for shipping, including the generation of shipping labels.
Explore tailored automation solutions, connect with our experts today!
Implementing Warehouse Automation
- Assessment and Planning: Evaluate operations, set objectives, and estimate budget.
- Technology Selection: Research and choose suitable automation.
- System Design: Plan warehouse layout and customize solutions.
- Implementation: Pilot tests and phased automation rollout.
- Training and Change Management: Train staff on new systems and communicate changes.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Monitor performance, gather feedback, and make improvements.
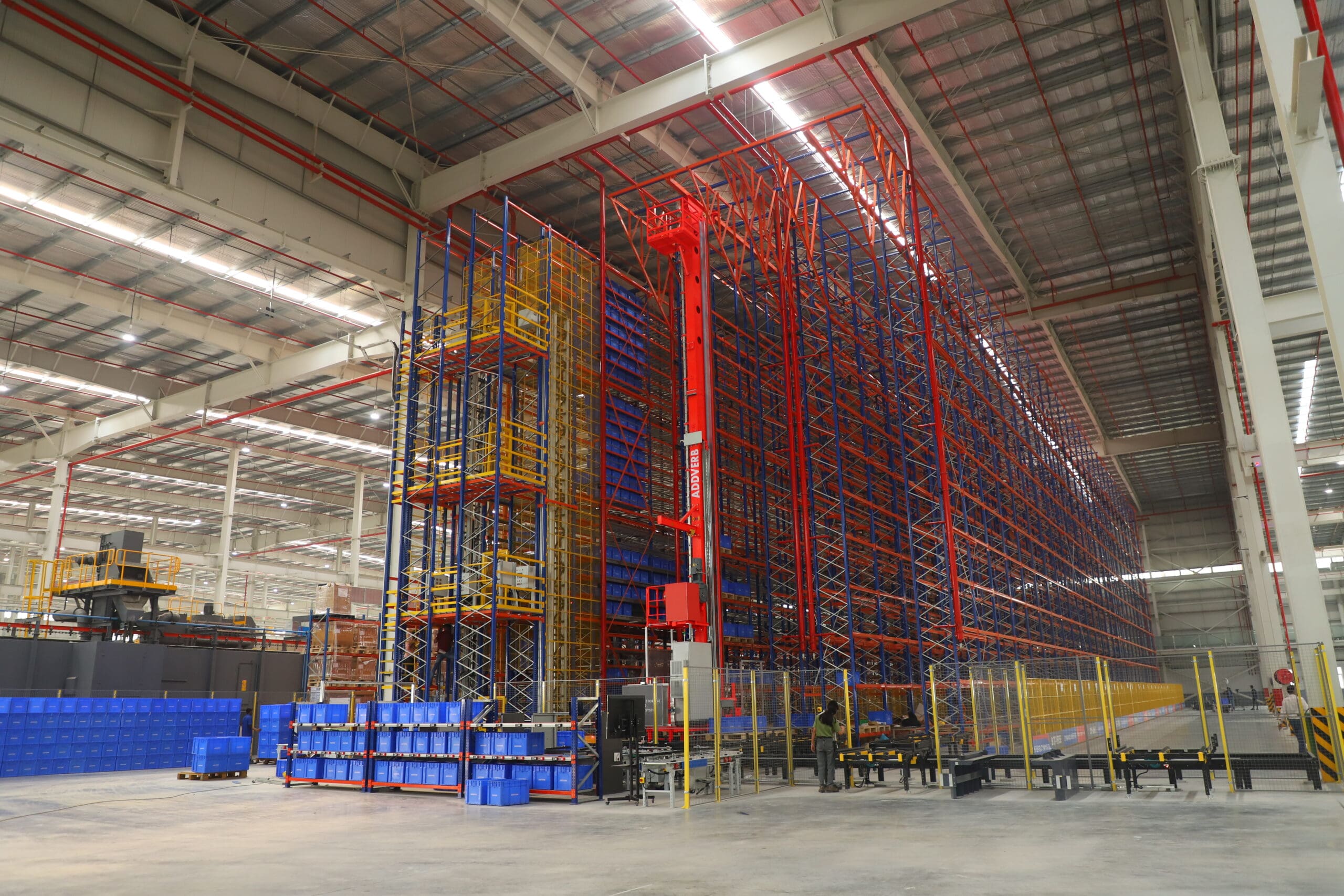

Discover the power of Addverb’s automated warehouse robots and elevate your warehouse efficiency and performance – why wait any longer?
Overcoming Challenges in Warehouse Automation
Although warehouse automation has various advantages, firms may face problems during implementation:
- Huge Investment: The initial investment in warehouse automation can be large, especially for smaller organisations. Long-term advantages and cost savings, on the other hand, frequently outweigh the initial outlay.
- Updated Knowledge: Integrating different automation technologies and maintaining compatibility with current systems can be difficult. Careful planning and communication with knowledgeable automation providers are required.
- Training: Employees may be concerned about job displacement or skill gaps as a result of automation. Proper training and communication are required to assist the workforce.
- Maintenance and Support: Automated systems necessitate routine maintenance and on-demand technical assistance. Businesses must have proper support channels in place to address any technological issues as soon as they arise.
- Changing Market Demands: To adapt to new technologies and develop their automation capabilities in response to quickly changing market demands, warehouses must be nimble in adapting to new technologies and expanding their automation capabilities.
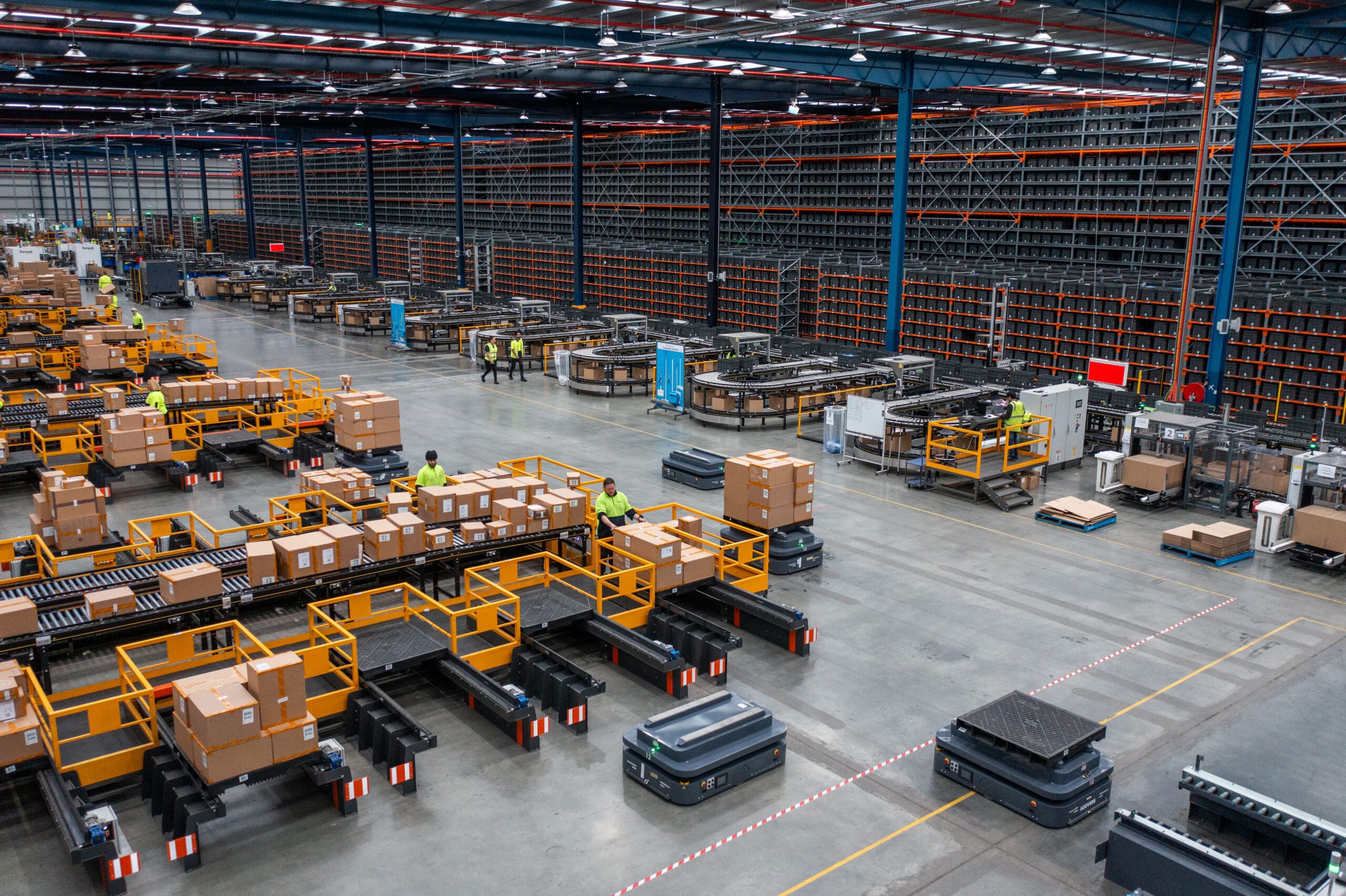

Future Trends in Warehouse Automation
The future of automated warehouses presents promising prospects, with technological breakthroughs fueling innovation. The following are some of the significant trends that are likely to shape the industry:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI-enabled solutions will allow warehouses to optimise operations better. Machine learning algorithms will analyse data to estimate demand, improve routing, and improve decision-making processes.
- Collaborative Robotics: The use of collaborative robots, or cobots, capable of working securely alongside humans will become more frequent.
- Autonomous Drones and Delivery Robots: Autonomous drones and delivery robots will play a key role in last-mile delivery, decreasing transportation costs and speeding up the process.
- RFID-enabled Wearable Devices: These devices will offer hands-free inventory tracking, allowing workers on the road to get real-time data and directions.
- Blockchain Technology: It will boost supply chain transparency by assuring trust and traceability throughout the logistics process.
Conclusion
The integration of warehouse automation technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) is profoundly impacting the logistics industry. By leveraging these advancements, organizations are experiencing significant improvements in operational efficiency, productivity, and accuracy throughout their supply chain processes. Despite the upfront investment, the long-term advantages and flexibility of these systems position them as crucial assets for contemporary transportation companies. Embracing smart warehouses not only streamlines operations but also empowers businesses to deliver exceptional customer experiences, ultimately positioning them ahead of the competition in the marketplace.
FAQ
What is warehouse automation?
Warehouse automation involves using robotics, artificial intelligence, and IoT devices to streamline warehouse operations, reduce manual labor, and increase efficiency.
How does automation improve efficiency in warehouses?
Automation enhances efficiency by speeding up order fulfillment, minimizing errors, optimizing inventory management, and reducing downtime through predictive maintenance.
Are there any challenges associated with implementing warehouse automation?
Initial costs and installation challenges are common, but the long-term benefits and savings typically outweigh these initial hurdles.
How does warehouse automation affect inventory management?
Automation improves inventory management by providing real-time data, reducing stock discrepancies, and ensuring optimal stock levels.
Can warehouse automation adapt to changing market needs?
Automated systems are highly adaptable and can be reprogrammed or upgraded to meet evolving market demands and business requirements.
How does warehouse automation contribute to better customer experiences?
Faster, more accurate order fulfillment and better inventory management lead to quicker delivery times and fewer errors, resulting in improved customer satisfaction.
Why is it important for logistics companies to adopt warehouse automation?
To remain competitive in a rapidly changing global economy, logistics companies must adopt automation to achieve higher efficiency, productivity, and adaptability.







