Table of Contents
Warehouse management, like any other management position, is about identifying the most important KPIs that affect business performance. Additionally, it involves providing the tools and resources required to meet those KPIs.
If we talk about an already live warehouse, the available space becomes the major criterion for choosing between dense racking systems and conventional racking systems. But when it comes to managing storage in general, this choice is dependent on two factors, viz., inventory characteristics like shelf life and count of SKUs; and Operational goals like fast delivery, low costs, etc. Before moving further, let us first describe how conventional and dense racking systems are defined:
What is Conventional Racking?
Selective pallet racking, or conventional racking, is the most used warehouse storage system. It gives direct access to all pallettes, and can be used in warehouses with a lot of SKUs (stock-keeping units).
Advantages of Conventional Racking
Accessibility: It offers each pallet direct access, making this a very good fit for a high SKU variety.
Versatility: Almost any product type.
Low Initial Cost: They are easier and cheaper to install and maintain.
Disadvantages of Conventional Racking
Low Storage Density: It needs more floor space between racks because there is aisles between racks.
Space Utilisation: Cannot maximise vertical and horizontal space sustainably.
What is Dense Racking?
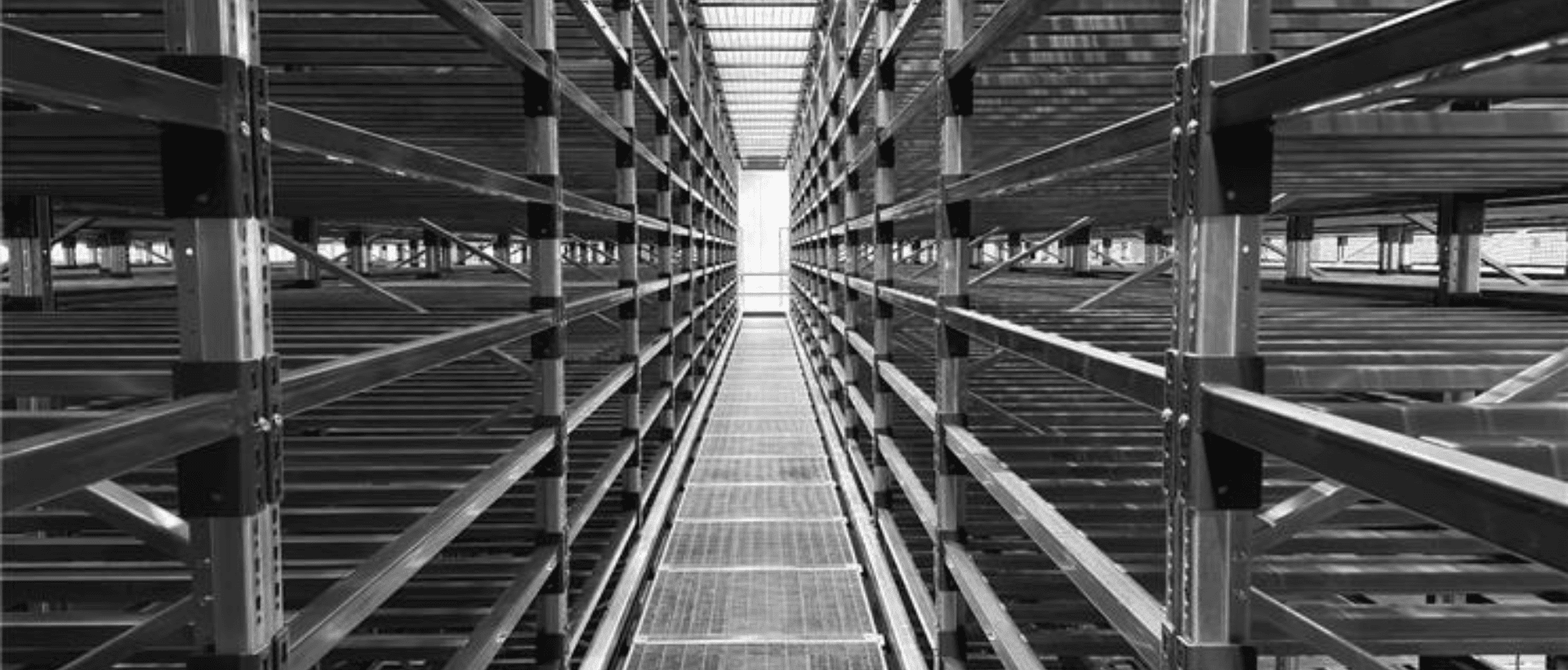
Dense racking systems, such as drive-in, drive-through, push-back, or pallet flow, aim to maximise storage density. They save aisle space and make better use of both vertical and horizontal space.
Advantages of Dense Racking
High Storage Density: A perfect place to store products that are of the same type in large numbers.
Space Efficiency: It reduces footprint of storage, freeing up floor and vertical space.
Customizable Flow: An inventory system can be built to support FIFO (First in, first out) or LIFO (last in, first out).
Disadvantages of Dense Racking
Selective Access: Specific pallets may be harder to retrieve.
Complexity: It requires trained staff and requires specialised handling equipment.
Higher Investment: Lower density compared to conventional racking.
Key Differences Between Dense Racking and Conventional Racking
| Feature | Dense Racking | Conventional Racking |
| Storage Capacity | High-density storage for bulk items. | Lower density, more suited to variety. |
| Accessibility | Limited access to specific pallets. | Direct access to every pallet. |
| Inventory Flow | High-volume, fast-moving inventory. | High selectivity, suitable for low-volume or varied SKUs. |
| Space Utilisation | Maximises vertical and horizontal space. | Requires more floor space due to aisles. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment. | Lower upfront cost. |
Popular Bulk Storage Warehouse Racking Systems
Selective Racks
Selective racks are the most commonly used pallet system, offering access from an aisle. They are ideal for narrow aisle racking, standard systems, and deep-reach systems. Selective racks require special narrow lift trucks and accommodate a single pallet in depth. This system has the lowest storage capacity of pallets & also the lowest cost per pallet; however, it is not scalable and will be expensive when the no. of pallet positions exceeds 3000. However, with more pallet positions and product lines, dense racking offers greater cost optimization, reducing storage costs by 20–50%.
According to grand view research the selective pallet segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 45.0% in 2024.
Drive-In and Drive-Through Racks
Drive-in racks are used for high-density storage and have one entrance and exit. These racks work well for LIFO storage. Drive-through racks, with access at both ends, are better suited for FIFO processes. Both systems require forklifts to move into the bay. However, they present safety concerns for forklift operators and are not suitable for small batches or a wide variety of products.
Push Back Racking Systems
Push-back racking systems are designed for bulk storage, typically storing 2-5 pallets. When a pallet is loaded, it pushes the next pallet back. The system operates on a LIFO basis and features inclined rails and sliding carts. Unlike drive-in systems, this system doesn’t require forklifts to enter the lanes, enhancing operator safety. However, the system has a limited reach, with a maximum of 4-5 access lanes.
Flow Racks
Flow racks, also known as gravity racks, are used for high-density storage, often up to 20+ pallets deep. Products are loaded at the higher end and removed at the lower end using a FIFO system. These racks operate on gravity rollers and do not require electricity. However, they are more expensive than conventional racking systems and have poor accessibility to all pallets.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
For high volume, low SKUs like FMCG or cold storage, you can use dense racking. if you manage a diverse inventory with frequent SKU turnover, go with conventional racking. Dense racking systems can take advantage of what space is left to optimise the area with reduced aisle requirements. Conventional racking is great for fast and frequent access. dense racking being the optimal choice for bulk storage efficiency.
Inventory Characteristics: Use dense racking for high-volume, low-SKU operations like FMCG or cold storage. Opt for conventional racking if you manage a diverse inventory with frequent SKU turnover.
Warehouse Space: If space is limited, dense racking systems can optimise available areas by reducing aisle requirements.
Operational Priorities: Conventional racking is ideal for fast and frequent access. Dense racking is the better choice for bulk storage efficiency.
Budget Considerations: Consider the long-term ROI. Dense racking has higher initial costs but provides greater space density, reduces running costs, and delays the need for warehouse expansion.
Conclusion
Both dense racking and conventional racking have their unique strengths and limitations. The choice depends on your operational priorities, inventory characteristics, and space availability. By understanding these systems and their applications, you can make an informed decision to enhance your warehouse’s storage efficiency and overall performance.
If you’re ready to transform your warehouse storage, explore advanced solutions with Addverb and maximize your operational potential!

FAQ
What is dense racking?
Dense racking systems, like pallet shuttles or drive-in racks, maximize space utilization by allowing high-density storage with minimal aisles.
What is conventional racking?
Conventional racking systems, such as selective or double-deep racks, prioritize accessibility and flexibility over density, with dedicated aisles for each row.
Which is more suitable for high SKU variety?
Conventional racking is better for high SKU variety, as it provides easy access to individual pallets.
Which racking system is better for cold storage?
Dense racking is ideal for cold storage due to its compact design, which minimizes cooling space and reduces energy costs.
How do dense racking systems impact material handling?
They often require specialized equipment like pallet shuttles or forklifts for efficient operation.
Are dense racking systems cost-effective?
Yes, they optimize storage capacity, reducing the per-pallet storage cost in the long run.





